In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) in Indore
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
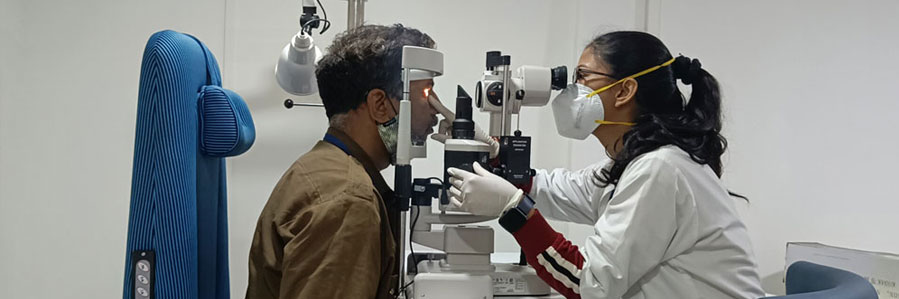
State of the art fertilisation centre
Jupiter Hospital is one of the most trusted names when it comes to delivering quality healthcare. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), more commonly known as ‘Test tube baby’ procedure, is one of the miraculous inventions of medical science which unconditionally transforms the way infertility is treated around the world. The best thing about medical science is that it gives you hope even when the chips are down. Nowadays many couples or parents are suffering from fertility disorders. IVF and other assisted reproductive technique (ART) are very helpful for couples facing such issues.
In Jupiter Hospital, we provide state-of-the-art care that is the best, as we have highly advanced medical facilities with experts in IVF who aim to give the best possible outcomes.
Team
Conditions treated with IVF
IVF was originally developed for women with blocked tubes or missing fallopian tubes and it is still the procedure of choice for these situations. It is also used when other conditions are present. There are certain fertility disorders in patients which can be treated with IVF and other assisted reproductive techniques (ART). If the couple is diagnosed with any of the following conditions, IVF can be an option for them.
Fertility Disorders in male:

Abnormal Sperm Count
The sperm count is considered low if it is below 15 million sperms per mL of semen. The normal sperm count is 40 million to 300 million sperm per mL of semen. Having a low sperm count decreases the odds that one of the sperm will fertilize the egg, resulting in pregnancy. Nonetheless, many men who have a low sperm count are still able to father a child. In some cases, total absence of sperms is observed, which is known as azoospermia.

Low Sperm Motility
Motility refers to a sperm's ability to get where it needs to go. For the sperm to get through the cervical mucus to fertilize a woman's egg, they need to have progressive motility of at least 25 micrometers a second. Poor sperm motility or asthenozoospermia is diagnosed when less than 32 percent of the sperm are able to move efficiently.
Causes of these disorders can be
Tobacco smoking, Drinking alcohol
There is an evidence that habits like tobacco smoking, drinking alcohol can damage the testicles. Smoking tobacco increases intake of cadmium, because the tobacco plant absorbs this metal. Cadmium, being chemically similar to zinc, may replace zinc in the DNA polymerase, which plays a critical role in sperm production. Zinc replaced by cadmium in DNA polymerase can be particularly damaging to the testes.
Environmental factors: Exposure to radioactive chemicals
Extended exposure to benzenes, toluene, xylene, herbicides, pesticides, organic solvents, painting materials and lead might contribute to low sperm counts. Exposure to radiation can reduce sperm production. It can take several years for sperm production to return to normal. With high doses of radiation, sperm production can be permanently reduced.
Hormone imbalances
The hypothalamus, pituitary and testicles produce hormones that are necessary for production of sperms. Alterations in these hormones, as well as in other systems such as the thyroid and adrenal gland, may impair sperm production.
Tumors
Cancers and nonmalignant tumors can affect the male reproductive organs directly, through the glands that release hormones related to reproduction, such as the pituitary gland, or through unknown causes. Surgery, radiation or chemotherapy to treat tumors also can affect male fertility.
Fertility Disorders in Female

Ovulation Disorders
Ovulating infrequently or not at all accounts for most cases of infertility. This can be caused by a problem with regulation of reproductive hormones or problems in ovary.
This can be caused by the following reasons -
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) causes a hormone imbalance, which affects ovulation.
- Excess physical or emotional stress, a very high or very low body weight, or a recent substantial weight gain or loss can disrupt production of hormones that are responsible for ovulation.
- Premature loss of eggs from the ovary

Tubal infertility
The damaged fallopian tube restricts the passage of sperms to the egg. The causes of this blockage includes
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Previous surgery in the abdomen or pelvis, including surgery for ectopic pregnancy.

Endometriosis
It is a disorder in which the tissues forming the lining of the uterus, i.e. the endometrium, grows outside the uterus. The most common symptoms are pelvic pain, often associated with periods and menstrual irregularities.

Unexplained fertility disorders
In some cases, in male as well as in female, the cause of infertility is not found. Such cases can also be treated with IVF and assisted reproductive technologies.
FAQ

Semen analysis
The semen sample is tested in a laboratory to check for the sperm count, motility etc. The urine sample may also tested for the presence of sperms.

Hormone test
The semen sample is tested in a laboratory to check for the sperm count, motility etc. The urine sample may also tested for the presence of sperms.

Genetic test
Genetic test are done to find out the genetic defect leading to infertility.

Biopsy
In some cases, testicular biopsy is done to extract the sperm for assisted reproductive technology and also to investigate the cause of infertility.

Radiology Investigation
Transrectal or scrotal ultrasound, or a test of the vas deferens (vasography) may be performed, if required.

Other
Other tests might be performed to check the quality of the sperm like DNA abnormalities.
Fertility Investigation tests for female:

Ovulation test
Blood tests are done to check the hormone level to understand whether the female is ovulating.

Hysterosalpingography
The test investigates the condition of uterus and fallopian tube. It checks for blockages or if any other abnormality present. The X-ray is taken to check whether the cavity is normal and if the fluid spills out of the fallopian tube.

Ovarian Reserve test
This test is performed along with the hormone testing in initial days of the menstrual cycle. It helps to determine the quantity of eggs available for ovulation.

Hormone test
These tests are done to check the level of the hormones that are responsible for reproductive processes.

Radiology Investigations
Ultrasounds are done to check for ovarian or uterine diseases. Sonohysterogram is done to see the details inside the uterus which are not usually seen by regular ultrasound.

Other
In rare cases, as per the situation, hysteroscopy or laparoscopy may also be required.
It is a type of artificial insemination, used to treat fertility disorders. This is the process in which the sperm from the partner or the donor is directly released into the uterine cavity. It is done around the time of ovulation.
During natural conception, sperms travel from the vagina through the cervix, into the uterus, and up to the fallopian tubes. With IUI, sperm sample is prepared and concentrated, and placed directly into the uterus, which puts them closer to the egg.
In this procedure, the best quality sperms are chosen from semen sample. The sample will be washed in a way that separates the highly active, normal sperm from lower quality sperm and other elements. Most of the IUIs are done a day or two after detecting ovulation, for the sperm to fertilize with the released egg. Depending on the reasons for infertility, the timing of IUI can be coordinated with normal cycle or with fertility medications.
The treatment is recommended for -- It is the right choice of treatment when the male partner is diagnosed with some fertility disorder like low sperm count, reduced motility, abnormal morphology of the sperm, erectile dysfunction.
- Endometriosis related infertility - For infertility related to endometriosis, using medications to obtain a good-quality egg along with performing IUI is often the first treatment approach.
- Cervical factor infertility -Some cervical abnormalities can restrict the entry of the sperm into the uterus. The thickened cervix can prevent sperm from reaching the egg and thereby reducing the chances of conception.
- Age - Fertility experts prioritize the IUI process to treat the age related infertility.
- Donor sperm -For women who need to use donor sperm to achieve pregnancy, IUI is most commonly used. Frozen donor sperm specimens are obtained from certified labs and thawed before the IUI procedure.
The procedure is done in a hospital, performed by IVF expert and specially trained nurse. It takes around 15 to 20 minutes. The IUI procedure itself takes around a minute or two and requires no medications or pain killers. The patient can get back to his normal daily activities on the same day after a short rest. Some light spotting can be observed in next two days after the procedure.
Results of IUI -After two weeks of the procedure, the at-home pregnancy test is done. The doctor may instruct to return in about two weeks for a blood test, which is more sensitive in detecting pregnancy after fertilization.
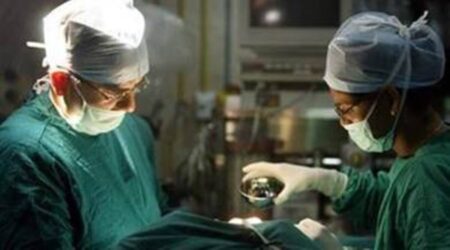
It is a complex series of procedures used to help with fertility or prevent genetic problems and assist with the conception of a child. In vitro fertilization, that is the test tube baby, is the procedure in which the fertilization is achieved outside the uterus. It is the most commonly used procedure to help couples facing fertility issues.
The procedure starts with monitoring the women for ovulation. The matured eggs are removed from the ovary. The frozen semen sample from the laboratory is prepared and it is allowed to fertilize the eggs in a culture medium in a laboratory. Once the egg is fertilized, and embryo is formed, it undergoes embryo culture for 2 to 6 days. Embryo is then implanted into the uterus to establish a successful pregnancy.
IVF is the most effective form of assisted reproductive technology (ART). The procedure can be done using a couple's own eggs and sperm or it may involve eggs, sperm or embryos from anonymous donor. In some cases, a gestational carrier — someone who has an embryo implanted in the uterus — might be used.
The treatment is recommended for -- As a primary treatment option for the women above the age of 40 years.
- Damaged/blocked fallopian tube - If the fallopian tube is damaged or blocked, it is difficult for a egg to be fertilized and for an embryo to reach the uterus. In such cases, the technique is used and embryo formed in the laboratory is implanted in the uterus.
- Ovulation disorder -If the ovulation is irregular or rare, the menstrual cycle is monitored and the matured egg is retrieved for the IVF. If the ovulation is totally absent, donor oocyte can be used for the IVF process in order to achieve the pregnancy.
- Cervical factor infertility -Some cervical abnormalities can restrict the entry of sperm into the uterus. The thickened cervix can prevent sperm from reaching the egg and thereby reducing the chances of conception.
- Endometriosis - It is a condition in which the tissues lining the uterus grow outside the uterus causing infertility in females. This can be treated with the technique of IVF.
- Genetic disorders -If any of the partner has a genetic disorder, which may be transferred to the child, then the IVF can be done along with other genomic procedures. The formed embryos are screened for the known genetic disorders. The embryos that do not have the identified genetic disorders can be transferred to the uterus.
Duration of the procedure - IVF involves several steps — ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, sperm retrieval, fertilization and embryo transfer. One cycle of IVF procedure takes around 2 to 3 weeks. More than one cycle may be needed.
The ProcedureOvarian stimulation -The cycle begins by using hormones or medication to stimulate ovaries to produce more eggs. Multiple eggs are required to increase the chances of fertilization. Generally, one or two weeks of ovarian stimulation is required before the eggs are ready for retrieval.
Egg Retrieval -It is done at the hospital, 36 hours after the final stimulation and before ovulation. The procedure can take around 20 minutes. Transvaginal ultrasound aspiration is the usual retrieval method. An ultrasound probe is inserted into patient’s vagina to identify follicles. Then a thin needle is inserted under ultrasound guidance to go through the vagina and into the follicles to retrieve the eggs.
Sperm retrieval - The semen sample from the male partner needs to be provided at the hospital on the day of egg retrieval.
If it is not possible to collect the sample by natural means, for example in cases like azoospermia (absence of sperm), several techniques are used for sperm retrieval.
Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA) And Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (PESA) -
If the hormonal profile is normal, in cases of obstructive azoospermia (absence of sperm), sperms can be aspirated through the testis or epididymis. It can be done under local anaesthesia. Sperms are separated from the semen sample. Donor sperms can also be used.
Fertilization - The retrieved sperm and eggs are kept together under laboratory conditions for fertilization.
There are two methods by which the fertilization is performed -- Conventional Insemination -
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) - It is the procedure in which the healthy sperm is directly injected into the cytoplasm of the egg.
Once the eggs are kept for fertilization, the next day, the embryologist will examine the eggs for fertilization and later on for further development of embryos. If there are more than three well developed embryos, it is possible to freeze them for a later transfer, if necessary.
The embryos are allowed to develop in incubator until they are ready for implantation.
Before the embryo gets transferred, there are certain procedures which may be required.
- LASER Hatching - If the outer shell of the embryo, i. e. blastocyte is tough, laser hatching is done on it when it reaches to day 5. It increases the chances of implantation and allows that embryo to implant into the uterus. That’s why laser hatching is advised to patient who have had more than two IVF (implantation) failures.
- Genetic Testing - A small sample of the embryo is taken and tested for specific genetic disorders or to correct the number of chromosomes, typically after day 5 or day 6. This reduces the chances of transmission of genetic disorder from parent to child.
Embryo Transfer - About three to five days after fertilization, the embryos will be placed in the uterus using a catheter. Embryos get settled in the lining of the uterus and begin to develop. Like other processes, this part of IVF is performed in hospital while the mother is awake.
Transfer of embryos that are more developed is associated with higher pregnancy rates compared with less-developed embryos (day two or three). However, not all embryos survive the development process. Hence more than one embryos are transferred.
A pregnancy test is done after 12 - 14 days of egg retrieval. If the test comes positive, the woman is further referred to an obstetrician for prenatal care.
To fertilize the egg, the sperm’s head has to get attached to the outer shell of the egg. From there the sperm cell will go inside of the egg, i.e. cytoplasm, where the fertilization will take place.
In cases of infertility, sometimes this outer layer of the egg is thick which makes it hard for a sperm to penetrate through it. In other cases, low sperm motility can be the cause for sperm being unable to reach the egg’s outer layer.
In such cases, intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) is done along with IVF, in which a single healthy sperm is injected directly into the cytoplasm of the egg. Once the egg is fertilized with the injected sperm, the further steps of IVF procedure are followed.












 View Map
View Map Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Health Check-up
Health Check-up





 Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Health Checkup
Health Checkup Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment